High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) is a condition in which there is too much glucose circulating in our blood, leading to deterioration in the functioning of the body. The most common cause of hyperglycemia is a gradually increasing disturbance in the body’s carbohydrate metabolism, resulting mainly from a poor diet and the associated overweight or obesity. Too high concentration of sugar in blood, especially when it appears with increasing frequency, is a dangerous phenomenon. It results in a number of diseases with diabetes at the top of the list. Severe hyperglycemia can threaten our life and health. However, elevated sugar level is a state, which in many cases can be reversed, even in case of diagnosed diabetes. How to lower sugar? How to lower blood glucose levels and regain good mood?
Table of contents
- 1 Hyperglycemia – what is it and what is its cause?
- 2 Too high sugar – a problem that cannot be ignored
- 3 Normal blood sugar and hyperglycemia
- 4 The most common symptoms of hyperglycemia
- 5 Causes of hyperglycemia
- 6 Hyperglycemia – what tests should be done?
- 7 How to reduce high blood sugar? How to prevent diabetes?
Hyperglycemia – what is it and what is its cause?
Too high level of sugar in blood (also called hyperglycemia or overdiagnosis) is a state, in which in our blood there is more than normal concentration of glucose. The higher the sugar level, the worse the body works and the more severe the symptoms.
Hyperglycemia is usually caused by poor diet and unhealthy lifestyle, but it may also be related to hormonal fluctuations, metabolic disorders, or inflammation occurring in the body. It may also be the effect of certain diseases or the use of certain medications.
Too high sugar – a problem that cannot be ignored
As it has already been mentioned, the increase of glycemia is most often caused by an improper diet, in which carbohydrates with a highAs already mentioned, the increase in glycemia is most often caused by an inappropriate diet, which is dominated by carbohydrates with a high glycemic index, fatty and highly processed food and at the same time, not enough dietary fiber.
Diabetic disorders usually develop gradually. After a meal rich in simple sugars, one suddenly feels sleepy and tired, and then there is increased gastric suction and a strong desire to eat something (preferably sweet). With time, these incidents become more frequent, the problem of easy and fast gaining of weight appears, the level of sugar in blood fluctuates more often and more violently.
In order to normalize the level of glucose in the blood, the body begins to secrete more and more insulin (this hormone is responsible for delivering glucose to the cells, which results in lowering the level of sugar in the blood). However, the cells become more and more resistant to the action of insulin, and the blood glucose level is still elevated and it becomes harder and harder to bring it down. This is how insulin resistance develops, then it turns into pre-diabetes, which then turns into type 2 diabetes.
If too high sugar is a problem that concerns us as well, it is worth to start fighting with it at once. The earlier you change your diet and reduce your body weight, the better chances you have to avoid severe form of diabetes and its complications.
Normal blood sugar and hyperglycemia
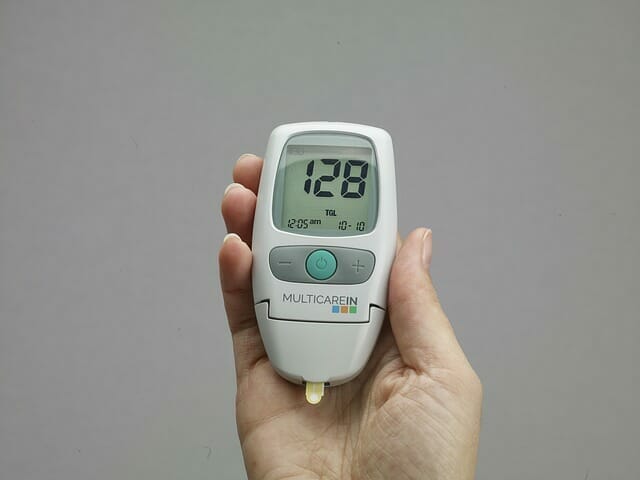
More frequent and more intense symptoms of hyperglycemia (over-sugarosis) and hypoglycemia (under-sugarosis) are an alarm signal that something is wrong with the carbohydrate metabolism in the body. We can check the level of glucose in the blood with a glucometer or with the help of special laboratory tests.
When can we talk about hyperglycemia, and when is the blood sugar level normal?
For adults, the normal fasting blood sugar level is 70-99 mg/dl (this is the normal fasting blood sugar level)
When the fasting blood sugar level measured is between 100-125 mg/dl, it tells us about abnormal fasting blood glucose (IFG) and pre-diabetic state.
When the fasting blood sugar level (in two measurements) is higher than 126 mg/dl, it means diabetes.
And when it comes to blood sugar levels after a meal (two hours after), a result below 140 mg/dl is considered normal.
When the blood glucose level two hours after a meal is between 140-199 mg/dl, it indicates pre-diabetes.
When the blood glucose level measured two hours after a meal is greater than 200 mg/dl, this indicates diabetes.
The given blood sugar standards apply to adults. It is worth mentioning that for the elderly, these norms look a little different, they are a little broader. For example, the norm of fasting blood glucose for the elderly is 80-140 mg/dl, and after a meal – less than 180 mg/dl.
The most common symptoms of hyperglycemia
Symptoms of hyperglycemia occur when there is a lack of insulin in the body, or when cells do not respond to the action of insulin and therefore blood glucose levels cannot be reduced.
Symptoms of abnormal high blood glucose levels may occur shortly after eating a meal high in easily digestible carbohydrates, or they may occur (The longer your body is unable to reduce sugar, the worse and more dangerous the symptoms will be).
Symptoms of high blood sugar:
- feeling tired,
- weakness,
- feeling worse,
- problems concentrating,
- drowsiness,
- headaches and dizziness,
- increased thirst,
- excessive appetite,
- dry mouth,
- frequent urination,
- visual disturbances,
- nausea and vomiting,
- skin problems (often recurrent skin infections, excessive dryness of the skin, itching of the skin),
- frequent urinary and genital tract infections,
- difficulties with wound healing.
Causes of hyperglycemia

Too high blood sugar is a consequence of disorders in insulin management (insulin deficiency or insufficient insulin action on tissues and cells). The most common cause of hyperglycemia is improper diet, but this phenomenon can also have other causes.
Main causes of high sugar:
- Type 1 diab etes – an autoimmune disease in which immune cells attack the pancreatic cells responsible for insulin production. Insulin deficits in type 1 diabetes are a direct contributor to elevated blood glucose. Skipping a dose of insulin, or too little insulin, are factors that can cause severe hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes. This can lead to life-threatening complications (ketoacidosis, ketoacidosis coma). Accumulation of glucose in the blood can also cause neuropathy and damage to blood vessels, loss of vision.
- Type 2 diabetes is a civilization disease caused by obesity, bad diet, unhealthy lifestyle. The following factors may contribute to the occurrence of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: discontinuation of treatment, improper selection of drugs, skipping insulin doses, ignoring the recommendations of the diabetic diet, taking too little antidiabetic preparations.
- Dietary mistakes – eating too many meals, too many products rich in simple sugars in theeating too many meals, too many products rich in simple sugars in the menu, too many flour and fatty products in the menu, a menu based on highly processed dishes.
Additional factors that may cause hyperglycemia are:
- stress,
- lack of physical activity, sedentary lifestyle,
- alcohol abuse,
- certain diseases, inflammatory conditions in the body, infections, severe pain,
- hormonal disorders,
- metabolic disorders,
- pregnancy.
Hyperglycemia – what tests should be done?
There are a number of tests for people who notice symptoms characteristic of hyperglycemia and would like to check whether they have insulin resistance, diabetes, or pre-diabetes.
Tests to diagnose diabetes and pre-diabetes
- fasting glucose test,
- fasting insulin levels,
- oral glucose tolerance test (fasting and two hours after drinking a glucose solution),
- blood glucose,
- glycated hemoglobin,
- metabolic buckle method,
- HOMA-IR index,
- lipid profile.
How to reduce high blood sugar? How to prevent diabetes?
High sugar diet

Both in the early problems with hyperglycemia and in the prevention of diabetes, the most important thing is to reduce body weight to a normal level and to change eating habits and eliminate foods that contribute to rapid fluctuations in sugar levels.The most important thing, both for early problems of hyperglycemia and for prevention of diabetes, is to reduce body weight to a normal level and to change eating habits and eliminate foods that contribute to rapid fluctuations in blood glucose levels (foods with a high glycemic index).
Products not recommended for people struggling with high blood sugar:
- sweets,
- white flour products (e.g. white bread and white rolls, white pasta, confectionery),
- white rice and fine groats (e.g. semolina),
- very ripe and very sweet fruit,
- sugar, honey, jam,
- sweet coloured drinks and juices with added sugar,
- sweetened yoghurts and dairy desserts,
- French fries, baked potatoes,
- chips, sticks and other salty snacks,
- sweetened breakfast cereals,
- corn flakes,
- fatty meats and cold cuts,
- low-quality meats, canned goods,
- fast food,
- ready meals.
Products recommended for people struggling with high sugar:
- vegetables (in large quantities),
- less sweet and less ripe fruits (in moderation),
- wholemeal bread,
- wholemeal pasta,
- brown rice,
- seeds and seeds (e.g. pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, linseeds),
- natural oatmeal,
- bran,
- yogurts with no added sugar, kefir, buttermilk,
- cheeses,
- eggs,
- lean meat,
- leaner, good quality cold cuts.
Physical activity and high sugar
Very important with problems with high sugar is to break with a sedentary lifestyle. Low physical activity is a factor that significantly affects the development of diabetes, and vice versa – systematic physical activity reduces the risk of diabetes and reduces insulin resistance.
During exercise (even moderate), the cells of our body have a higher demand for glucose, which is the energy material for them. So they consume glucose more intensively, and thus the level of sugar circulating in the bloodstream is reduced.
What is important, if we are trying to reduce the level of sugar in the blood, it is also worth taking care of proper relaxation, avoiding stress and exhaustion, and getting a good night’s sleep. These seemingly insignificant factors have a big influence on the carbohydrate metabolism in the body. Good psychophysical condition is an ally of more stable, lower blood sugar levels.
Natural ways to deal with high sugar
The goal of diabetes treatment is to stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent hyperglycemia. Special plant extracts, which improve insulin-glucose metabolism in organism, can be a great support in the process of sugar reduction. Multicomponent dietary supplements based on these extracts also work very well.
The best natural ingredients that help regulate blood sugar levels:
- white mulberry,
- ginger,
- berberine,
- Garcinia cambogia,
- dandelion,
- cinnamon,
- fenugreek,
- apple cider vinegar.
Meet Redusugar – an innovative preparation containing 9 of the most effective natural substances lowering blood sugar levels

Sources:
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/low-blood-sugar-treatment.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/low-blood-sugar.html
- https://www.healthline.com/health/type-2-diabetes/hyperglycemia

