Although it does not cause skin changes, alopecia areata is an inflammatory disease that results in sudden, localized hair loss. It can affect adults and children, and is often suffered by women for whom it is a real nuisance.
Table of contents
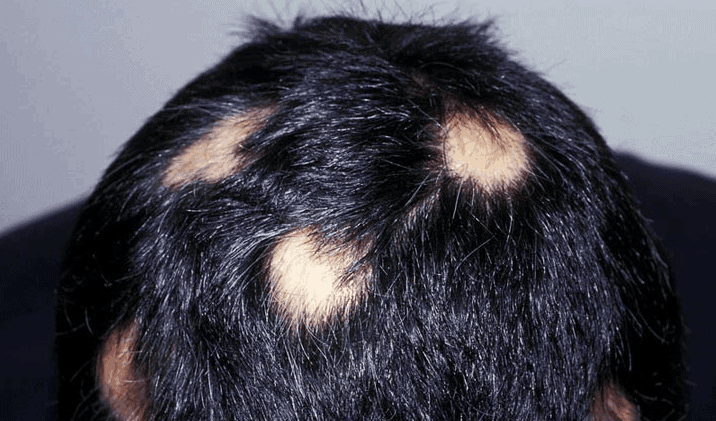
Examples of alopecia areata
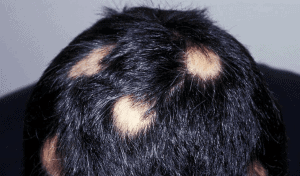
There is no clear evidence so far pointing to specific causes of sudden focal alopecia, although recent studies seem to confirm that it is an autoimmune disease. Abnormal functioning of the immune system causes it to attack hair follicles recognizing them as foreign bodies.
This hypothesis seems to be supported by the fact that alopecia areata is often accompanied by other autoimmune diseases such as lupus erythematosus, atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, thyroiditis, and others. Genetic factors are also mentioned as one of the causes of alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata – symptoms
Sudden hair loss, sometimes within a few days or even hours, is a characteristic and visible symptom of this disease. The first “pancake” is usually round and small, with time it is joined by other foci of different size and shape. In most cases they occur on a limited area of the scalp, sometimes they may appear on other hairy areas of the body.
These lesions are unpredictable and may appear suddenly followed by spontaneous hair regrowth, or they may recur at irregular intervals – this is called recurrent alopecia areata.
Treatment of Alopecia Areata
General and topical treatments are used to promote hair regrowth. This includes hair growth pills (e.g. Profolan), various liquids to rub into the scalp, therapies such as micro-needle mesotherapy, cryotherapy, acupuncture, ultraviolet light therapy. Various immunosuppressive preparations such as cyclosporine or corticosteroids are also used.
Female pattern baldness
When it comes to children and adolescents, both girls and boys are more or less equally exposed. However, among adults, ladies are unfortunately more likely to fall victim to alopecia areata. Due to the particular aesthetic context, in the case of women, the doctor should pay close attention to the probable cause of the condition and the use of various cosmetic techniques and, if necessary, sedative drugs.
The idea is, on the one hand, to provide a comprehensive therapy for the best possible efficacy, on the other hand, to minimize the stress associated with the disease. In addition to the specialized pharmaceuticals indicated by the doctor, women (and not only) can also resort to traditional folk methods, for example, juice from onions, garlic or black radish, red pepper tincture, croton oil.