How to lower cholesterol? This question is asked by a whole host of patients when faced with abnormal blood test results. Elevated cholesterol is one of the most commonly observed health problems today. Its cause is most often poor diet, overweight and excess stimulants. Unfortunately, too high cholesterol is a dangerous phenomenon, especially if it accompanies us for a long time. It is a prelude to serious cardiovascular diseases and syndromes such as heart attack or stroke. However, there is also good news – in the fight against high cholesterol, simple home remedies and readily available dietary supplements based on natural extracts from relevant medicinal plants are very often helpful. Sometimes even small changes in dietary habits help to reduce cholesterol and improve the work of the circulatory system.
Table of contents
What is cholesterol?
By convention, the term “cholesterol” is used to refer to LDL cholesterol, the bad cholesterol responsible for the development of atherosclerotic plaques. However, there is also its beneficial fraction, namely HDL cholesterol. If the concentration of HDL cholesterol is high enough, our arteries and heart are well protected. What exactly is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is an organic chemical compound classified as a lipid (fatty) substance, or more precisely as a steroid. It is found in every cell of animal organisms and is needed for the proper functioning of the body. Its main task is to build and stabilize cell membranes, but it also plays several other roles, including:
- takes care of the proper functioning of the brain,
- takes part in the synthesis of many hormones and vitamin D,
- is part of the myelin sheath of neurons, affects the functioning of synapses,
- is one of the substrates necessary for the production of bile acids.
In the human body, cholesterol is found in blood plasma, tissues and organs such as the heart and brain, among others. It is produced in the liver (endogenous cholesterol), from which it is transported to the tissues. It is also supplied in food (exogenous cholesterol).
For cholesterol to benefit our health, its level must be low enough. If there is too much of it in the body, it begins to bring harm, including worsening the condition of blood vessels and increasing the risk of heart disease and other health problems.
Good and bad cholesterol. What are the standards for cholesterol in the blood?
Cholesterol is partly synthesized in the body, especially in the liver, intestines and skin, and partly supplied from outside, in foods. Its main sources are animal fats, meat products and eggs, and to a small extent dairy products.
The main forms of cholesterol found in the body
- Cholesterol HDL (the so-called good cholesterol) – high-density lipoproteins. Their function is to transport excess cholesterol to the liver, so that it can then be efficiently metabolized, used in the synthesis of bile acids or removed from the body.
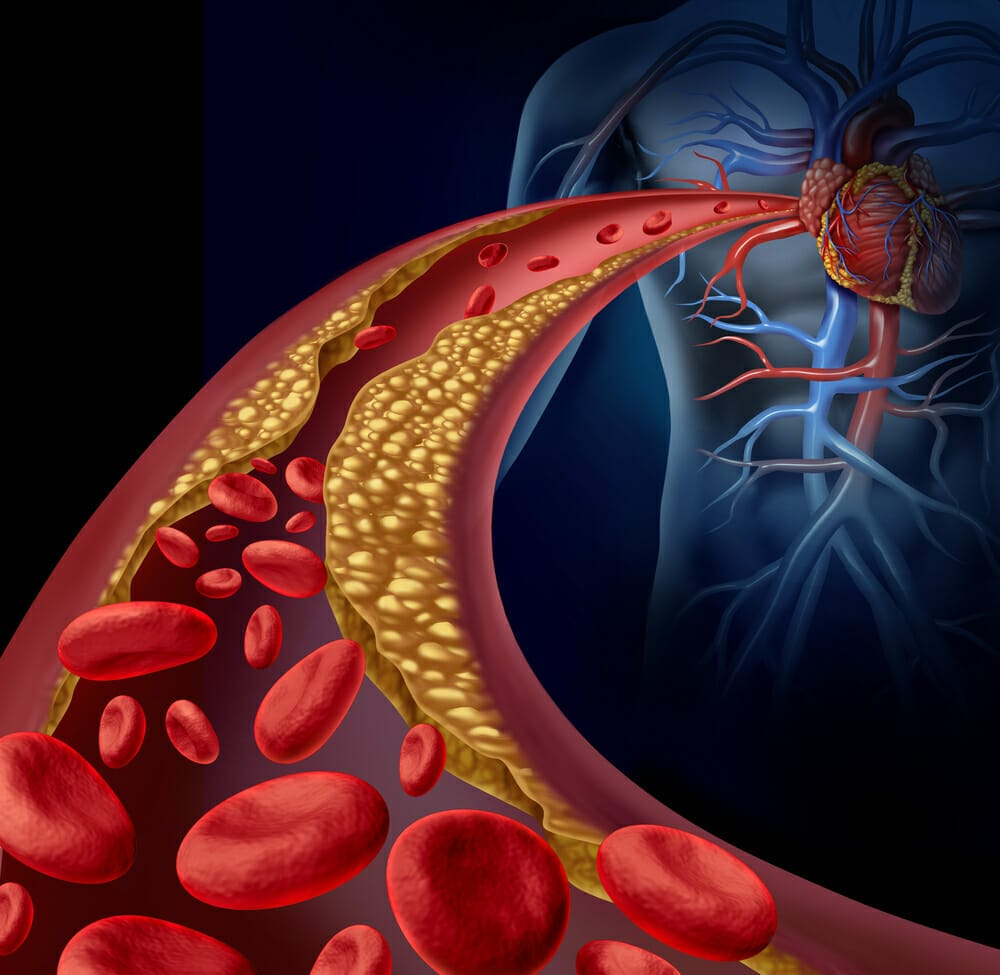
- Cholesterol LDL (so-called bad cholesterol) – low-density lipoproteins. Their role is to transport cholesterol into cells throughout the body. Excess LDL cholesterol accumulates in arterial vessels, forming atherosclerotic plaque.
Cholesterol – norms
And HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol are needed for the proper functioning of the body, but they must be within norms in order to do their job well. Particularly important is the level of LDL cholesterol. Its excess promotes the formation of atherosclerotic lesions, and can also be a factor in increasing the risk of heart attack, so it is advisable to systematically perform a lipid profile (lipidogram).
Lipid profile is a test in which, in addition to the concentration of good cholesterol HDL and bad cholesterol LDL, the level of triglycerides is also determined. All these indicators are information about the state of fat metabolism in our body and the potential risk of cardiovascular disease.
Norms of cholesterol LDL, cholesterol HDL and triglycerides:
- LDL cholesterol norm – less than 100 mg/dl (2.6 mmol/l)
- HDL cholesterol norm – more than 50 mg/dl (1.3 mmol/l)
- Triglyceride norm – less than 150 mg/dl (1.7 mmol/l)
Cholesterol HDL and cholesterol LDL together make up total cholesterol. The norm for total cholesterol in the body is 125 – 190 mg/dl. We should consider total cholesterol oscillating around 200-300 mg/dl as strongly alarming.
High cholesterol – causes, symptoms and effects
Excess LDL cholesterol is deposited on the walls of arterial vessels, including vessels responsible for supplying the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. Leading to hypertrophy of connective tissue and smooth muscle, LDL cholesterol narrows the lumen of the arteries, impairs blood flow and increases the clotting process (as a result, it promotes the formation of dangerous thrombi).
A prolonged state of elevated cholesterol is one of the main factors responsible for coronary heart disease and other life-threatening cardiovascular diseases.
Causes of high cholesterol
- a diet rich in unhealthy saturated fatty acids (their highest amounts are found in fatty meats, lard, butter, fatty meats),
- a large amount of fast food, highly processed foods and confectionery in the diet,
- diet low in dietary fiber,
- overweight, obesity,
- leading a sedentary lifestyle, too little physical activity,
- stress,
- alcohol abuse,
- smoking cigarettes.
A factor that raises the likelihood of having too high a blood cholesterol level is also the presence of certain diseases (e.g. kidney failure, hypothyroidism, diabetes, hypertension, liver disease with bile stasis) and the use of certain medications (e.g. glucocorticosteroids, antiepileptic drugs, contraceptive drugs).
Symptoms of high cholesterol
- Tight, shiny skin on the legs,
- pain and numbness in the legs,
- ulceration of the ankles,
- yellowish spots and thickening on the body (under the breasts, in the bends of the elbows, in the bends of the knees, around the eyelids),
- nodules on the tendons of the wrists and Achilles tendons,
- headaches and dizziness, weakness,
- problems with memory and concentration,
- sparse, slow-growing hair.
Consequences of elevated cholesterol
- tissue ischemia,
- atherosclerosis,
- ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease),
- stroke,
- ischemia of the lower extremities,
- myocardial infarction,
- peripheral artery disease.
How to lower cholesterol with home remedies?

High cholesterol is a significant health problem in modern society. It is estimated that up to 7 out of 10 people struggle with this ailment. Interestingly, the ailment is mainly associated with senior age, but it does not spare young people either. As early as 30 years old, cholesterol levels can rise and dangerous changes in the circulatory system can develop. No matter what age we are, cholesterol levels can be effectively lowered by simple means. In most cases, it is not necessary to reach for pharmaceuticals, but only lifestyle changes. This includes daily habits, exercise levels, as well as diet.
How to lower cholesterol with diet?
A proper diet is crucial in lowering cholesterol. If there are a lot of saturated fats and trans fats in our diet (supplied, for example, in the form of meat products and processed foods), the body is unable to effectively metabolize and excrete them from the body. As a result, they are deposited in the walls of the arteries, giving rise to atherosclerotic plaque.
To improve the metabolism of fats, and thus reduce the level of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood and inhibit the the development of atherosclerotic plaque, it is necessary to modify the diet, limiting the proportion of dangerous types of fats.
Above all, it is recommended to give up red meat (at the expense of fish and lean, white poultry meat), store-bought sweets and all ready meals and dishes for quick preparation. Menus should be built on the basis of vegetables and fruits. Whole-grain products should also be introduced as a substitute for white flour products.
In order to improve the lipid profile and improve the condition of the arteries, it is worth introducing into the menu large amounts of dietary fiber present, among others, in vegetables, fruits, whole-grain products, or thevegetables, fruits, whole grains, and the increasingly popular vital fiber(vital fiber is the crushed hulls and seeds of plantain and egg plant). Fiber positively influences food digestion processes, including fat digestion processes, stimulates the removal of fatty deposits and leads to a reduction in cholesterol levels.
Meet the richest vital fiber on the market: Fibre Select

An important role in an anti-cholesterol diet is also played by beneficial types of fats, mainly omega 3 fatty acids (contained, among others, in sea fish, grains and vegetable oils) which lead to an increase in the level of good cholesterol, while decreasing the level of bad cholesterol. It is also worth including in the menu products rich in B vitamins, vitamin C and vitamin A.
In an anti-cholesterol diet, dishes based on vegetables and legumes with healthy fats (e.g. cream soup of lentils and tomatoes with pumpkin seeds) and dishes based on seafood with plenty of vegetables (e.g. salad of mixed lettuce, avocado and smoked salmon, casserole of green vegetables and smoked mackerel).
To lower cholesterol, introduce foods such as:
- cereal products (such as oatmeal, rye, buckwheat, bran),
- groats (e.g. buckwheat, barley, oat, millet),
- vegetables,
- fruits,
- fatty marine fish,
- wholemeal and whole-grain bread, whole-grain pasta, brown rice,
- olive oil,
- vegetable oils (e.g., canola oil, flaxseed oil, thistle oil, hemp oil),
- seeds(flaxseed, plantain, sunflower),
- legumes,
- nuts.
Avoid such products and dishes as:
- fatty meat,
- fried dishes,
- heavy, greasy or floury sauces,
- lard,
- lard,
- hard margarines,
- fatty cured meats,
- canned foods, pâtés,
- offal,
- fast foods,
- salty snacks (e.g., chips),
- sweets (e.g., cookies, waffles, candy bars, candies),
- confectionery baked goods,
- prepared meals.
Limit the intake of such products as:
- eggs (especially dishes with liquid egg yolk),
- yellow cheeses,
- fatty milk,
- butter,
- cream,
- white bread,
- coconut oil.
How to lower cholesterol with natural means – herbs and supplements.

There is a whole range of natural remedies that can make lowering cholesterol a much faster process. They are commercially available in various forms, from powdered ingredients to herbal teas. We can also include ready-made capsules or tablets for lowering cholesterol in our diet if we lack the time to brew herbal infusions or make concoctions, and if we hope for instant results.
Ingredients particularly helpful in the fight against high cholesterol are:
- long oyster,
- common garlic,
- artichoke,
- olive,
- spotted thistle,
- choline,
- ginger,
- blanket,
- white mulberry,
- dandelion,
- alfalfa,
- fenugreek.
For better results, we can combine individual herbal ingredients or use ready-made preparations. One of the most interesting remedies on the market to help reduce cholesterol is Lipid Control Plus. It contains in its composition a rich composition of extracts that improve fat metabolism and stimulate the excretion of bad cholesterol and triglycerides from the body. The active ingredients not only help lower cholesterol, but also comprehensively support the heart and cardiovascular system and have a beneficial effect on the liver.
Get to know Lipid Control Plus
What else can we do to lower cholesterol?
Cholesterol normalization is also promoted by:
- regular physical exercise (e.g., light workouts 3-4 times a week, frequent walking, cycling, etc.),
- reducing body weight to an appropriate BMI value (BMI should be between 18.5 and 24.9 kg/m2),
- cessation of cigarette smoking,
- cessation or reduction of alcohol consumption.