Urinary incontinence is a common, embarrassing and unpleasant health problem. Although it is mainly associated with senior age, it actually affects people of all age groups. It involves a partial loss of bladder control, resulting in involuntary urination. In most patients, urinary incontinence has a very negative impact on well-being and quality of life. What are the causes and symptoms of urinary incontinence? How to combat this problematic ailment? Learn about treatment methods and home remedies for incontinence.
Table of contents
- 1 The problem of incontinence common among men and women
- 2 Causes and risk factors of incontinence. What can cause urinary incontinence?
- 3 Symptoms of urinary incontinence
- 4 Types of urinary incontinence
- 5 Effort incontinence
- 6 Urgency incontinence
- 7 Urinary incontinence from overflow
- 8 Urinary incontinence – tests.
- 9 Pharmacological treatments for urinary incontinence
- 10 Conservative treatment of urinary incontinence
- 11 Exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles (Kegel muscles)
- 12 Cosmetic and herbal products for incontinence
The problem of incontinence common among men and women
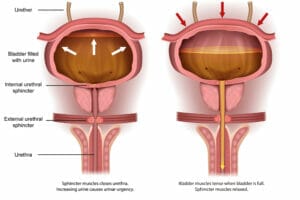
One of the most commonly observed conditions of the urinary system is urinary incontinence (urinary incontinence). This is an extremely persistent and very embarrassing condition, characterized by feeling a strong, uncontrollable need to urinate and the involuntary, uncontrolled flow of urine from the bladder. Trouble with proper urination is usually very annoying. They prevent the person struggling with them from functioning normally and negatively affect social relationships.
Urinary incontinence takes different forms and different degrees of severity. Most often, it is a long-term and refractory ailment. Sometimes, however, it appears only temporarily, briefly, in people who have normal daily bladder control, but as a result of some health turmoil, this control is momentarily disrupted. Such transient incontinence can also occur in pregnant women.
Usually, urinary incontinence is associated with conditions of old age. However, it can also be the result of many other diseases and have completely different causes. Many people of different ages struggle with urinary incontinence. The problem affects both sexes, but the ailment seems to be slightly more common in ladies. Statistics say that as much as 10-15% of the population struggles with incontinence.
Causes and risk factors of incontinence. What can cause urinary incontinence?
The factors responsible for the problem of incontinence are many. Urinary incontinence in women is most often associated with weakened pelvic floor muscles (in which case they do not tighten the urethra properly) and hormonal imbalances.
And in men, urinary incontinence is usually related to prostatic hypertrophy. Urinary incontinence can also be caused by other diseases, such as neurological conditions. It is often the result of bladder inflammation. The appearance of incontinence is also facilitated by the use of certain medications.
The most common causes and risk factors for incontinence are:
- overloading and weakening of the pelvic floor muscles (e.g., caused by frequent lifting or multiple pregnancies and childbirths),
- hypertrophy of the prostate gland (prostate) in men,
- significant overweight or obesity (too much weight contributes to excessive pressure on the muscles and bladder),
- pelvic surgery,
- hormonal changes,
- frequent constipation,
- urinary tract infections,
- other diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease),
- taking certain medications (e.g., diuretics),
- menopause period,
- alcohol and caffeine abuse,
- spinal cord injuries,
- certain forms of disability,
- history of stroke,
- dementia,
- old age.
Symptoms of urinary incontinence

Urinary incontinence can be mild or aggravated, or it can be a chronic or transient afflictiontransient, but the symptoms in almost all cases are the same, the main one being the leakage of urine from the urethra independent of our will.
Symptoms of urinary incontinence are:
- uncontrollable urine leakage,
- violent, strong, difficult to control urge on the bladder,
- involuntary urine leakage during coughing, sneezing, laughing,
- involuntary urine leakage during lifting and carrying heavy objects,
- urine leakage during increased physical activity, such as fast walking, jumping, running,
- nocturnal urge to push on the bladder, frequent visits to the toilet at night,
- frequent feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder,
- recurrent urinary tract infections,
- urinating in stressful situations, when nervous, during sleep.
Types of urinary incontinence
There are 3 main types of incontinence – stress incontinence, overflow incontinence and urgency incontinence, but there are also several additional, less common varieties. All types can have 3 different degrees of severity – low, medium or high. What are the most common types of incontinence?
Effort incontinence
Effort incontinence is a consequence of excessive strain and weakness of the pelvic floor muscles, which are responsible for controlling the flow of urine. The main symptom is involuntary leakage of urine during physical exertion and sports, as well as when coughing, sneezing, laughing. Common causes of stress urinary incontinence are: hormonal changes, certain diseases, prostate surgery, gynecological surgery, pregnancy, advanced age, obesity.
Urgency incontinence
The main cause of urge incontinence is the disturbed and increased activity of the bladder muscles. The symptom of the condition is a sudden, overwhelming need to urinate immediately (while the bladder is not necessarily overflowing).
The need to urinate immediately occurs in certain situations, such as during changes in body position, during sleep, during sexual intercourse, and most often leads to the involuntary leakage of a certain amount of urine. However, in some people struggling with urgency incontinence, urinary leakage does not occur. This form of incontinence most often occurs in men with an enlarged prostate gland, as well as in senior citizens.
Check out a multi-ingredient dietary supplement to support prostate health: Prostan Plus
Urinary incontinence from overflow
In this case, there is a partial blockage of the urine outflow mechanism, and thus the bladder is overfilled and the urine cannot continue to accumulate in it. There is then leakage of a certain amount of urine from the urethra. This type of incontinence often occurs in men with prostate disease and in cases of urethral stricture.
Other types of incontinence are:
- reflex incontinence (unconscious leakage of urine as a result of spontaneous, excessive contractions of the urinary detrusor muscle),
- functional urinary incontinence (in people unable to use the toilet normally, such as in the case of mental illnesses, reduced mobility, environmental factors, but without pathology in the urinary system itself).
- Mixed urinary incontinence (the combined occurrence of urgency and stress urinary incontinence),
- multifactorial incontinence (spontaneous leakage of urine as a result of the occurrence of several different factors, such as diseases, medication and old age),
- bedwetting (urination during sleep, such as in children),
- transient incontinence (short-term urine leakage occurring as a result of the onset of urinary tract infections, constipation, taking medications and disappearing immediately after the cause is resolved).
Urinary incontinence – tests.
Proper diagnosis is extremely important in the case of urinary incontinence. It allows you to accurately determine the cause of the ailment and choose the right treatment methods. To begin with, general urine and blood tests are performed to detect potential infections and identify possible other health problems. However, this is not all. The diagnostic process also includes:
- a medical history (the doctor asks the patient about the intensity of the problem, type of symptoms, frequency of symptoms, etc.),
- physical examination (e.g., abdominal examination with assessment of bladder filling),
- ultrasound examination (evaluation of the structure of the bladder, ureters, kidneys, prostate gland),
- a micturition diary (the patient records the amount and timing of fluids consumed and the frequency of urination),
- insertion text,
- cough test,
- urodynamic testing (urine flow test with evaluation of bladder and urethral function),
- cystoscopy (using a thin, tubular instrument inserted into the urethra to assess the condition of the bladder).
Pharmacological treatments for urinary incontinence
Treatment of incontinence can be based on pharmacological agents or involve certain procedures, depending on the cause of the condition.
Pharmacological treatment of urinary incontinence is usually based on the administration of antimuscarinic drugs that reduce the urge to urinate on the bladder.cher, decreasing the activity of the detrusor muscle and increasing the volume of the bladder. In some cases, adrenergic drugs are used to affect the relaxation of the detrusor muscle cells, thereby reducing bladder pressure. Other methods include injecting the bladder with botulinum toxin and estrogen treatment.
Surgical treatment is used infrequently, mainly when other methods have failed.
Conservative treatment of urinary incontinence
Conservative treatment is usually used as the first step to combat incontinence, even before drug treatment. Conservative treatment usually yields good results, especially if the ailment is not too severe.
Conservative treatment involves certain lifestyle changes, systematic implementation of certain behaviors by the patient, and the use of massage and physiotherapy treatments to regain bladder control and eliminate persistent symptoms.
Conservative treatment includes:
- weight reduction (for obesity and overweight),
- introducing a healthy diet,
- getting rid of constipation,
- performing pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegel muscles),
- limiting the use of stimulants,
- electrostimulation,
- biofeedback,
- medical massage.
Exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles (Kegel muscles)
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles with simple exercises is an effective method to increase bladder control and reduce urine leakage. These exercises mainly consist of alternately tensing and relaxing the internal pelvic muscles. The tensing mechanism is very similar to the mechanism that allows us to inhibit the flow of urine.
We tense the pelvic floor muscles for a few seconds, then relax them. We repeat the exercise 10 times. Do the workout every day, preferably in several series. Remember to try to tighten only the inner muscles without tensing the muscles of the buttocks, thighs or abdomen.
Cosmetic and herbal products for incontinence
If we take up the fight against incontinence by natural means, properly selected herbs, as well as ready-made, multi-ingredient preparations to support urinary health can be extremely helpful. One of them is Urinofix. It contains a set of valued medicinal plants that act to strengthen and relax the muscles of the urinary tract, as well asas well as herbs that reduce bladder pressure, fight infections and increase control of urine leakage. This is a comprehensive and effective yet natural support for the urinary tract.
In order to avoid embarrassing situations and maintain a high level of hygiene at all times, it is also worth using special pads and diapers designed for people struggling with incontinence.
Sources:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/urinary-incontinence
- https://www.healthline.com/health/overactive-bladder-vs-urinary-incontinence-vs-uti
- https://www.webmd.com/urinary-incontinence-oab/types-of-urinary-incontinence
- https://www.webmd.com/urinary-incontinence-oab/treatment-for-urinary-incontinence

